Newer
Older
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
423
424
425
426
427
428
429
430
431
432
433
434
435
436
437
438
439
440
441
442
443
444
445
446
447
448
449
450
451
452
453
454
455
456
457
458
459
460
461
462
463
464
465
466
467
468
469
470
471
472
473
474
475
476
477
478
479
480
481
482
483
484
485
486
487
488
489
490
491
492
493
494
495
496
497
498
499
500
501
502
503
504
505
506
507
508
509
510
511
512
513
514
515
516
517
518
519
520
521
522
523
524
525
526
527
528
529
530
531
532
533
534
535
536
537
538
539
540
541
542
543
544
545
546
547
548
549
550
551
552
553
554
555
556
557
558
559
560
561
562
563
564
565
566
567
568
569
570
571
572
573
574
575
576
577
578
579
580
581
582
583
584
585
586
587
588
589
590
591
592
593
594
595
596
597
598
599
600
601
602
603
604
605
606
607
608
609
610
611
612
613
614
615
616
617
618
619
620
621
622
623
624
625
626
627
628
629
630
631
632
633
634
635
636
637
638
639
640
641
642
643
644
645
646
647
648
649
650
651
652
653
654
655
656
657
658
659
660
661
662
663
664
665
666
667
668
669
670
671
672
673
674
675
676
677
678
679
680
681
682
683
684
685
686
687
688
689
690
691
692
693
694
695
696
697
698
699
700
701
702
703
704
705
706
707
708
709
710
711
712
713
714
715
716
717
718
719
720
721
722
723
724
725
726
727
728
729
730
731
732
733
734
735
736
737
738
739
740
741
742
743
744
745
746
747
748
749
750
751
752
753
754
755
756
757
758
759
760
761
762
763
764
765
766
767
768
769
770
771
772
773
774
775
776
777
778
779
780
781
782
783
784
785
786
787
788
789
790
791
792
793
794
795
796
797
798
799
800
801
802
803
804
805
806
807
808
809
810
811
812
813
814
815
816
817
818
819
820
821
822
823
824
825
826
827
828
829
830
831
832
833
834
835
836
837
838
839
840
841
842
843
844
845
846
847
848
849
850
851
852
853
854
855
# face-api.js
[](https://travis-ci.org/justadudewhohacks/face-api.js)
[](https://slack.bri.im)
**JavaScript face recognition API for the browser and nodejs implemented on top of tensorflow.js core ([tensorflow/tfjs-core](https://github.com/tensorflow/tfjs))**
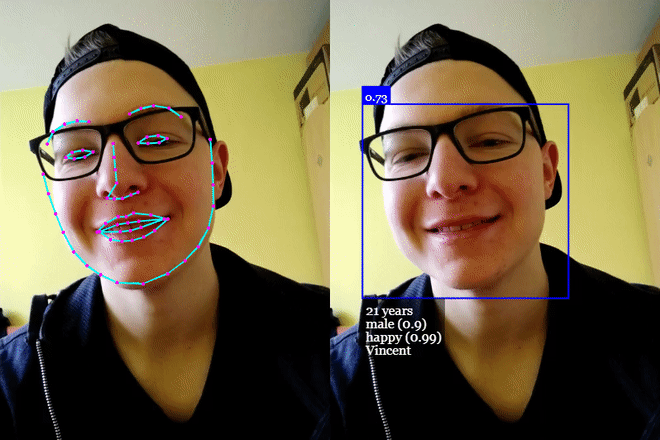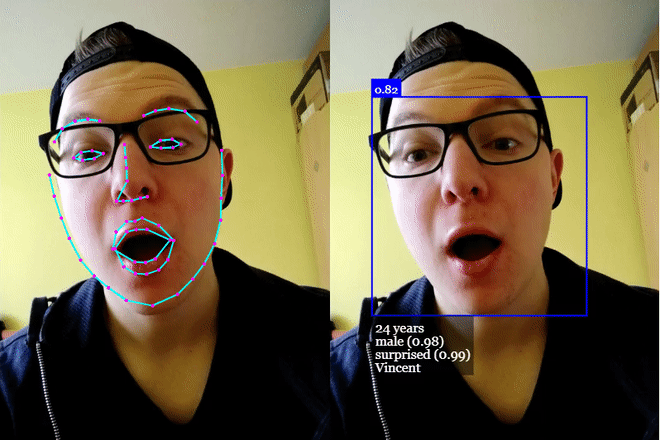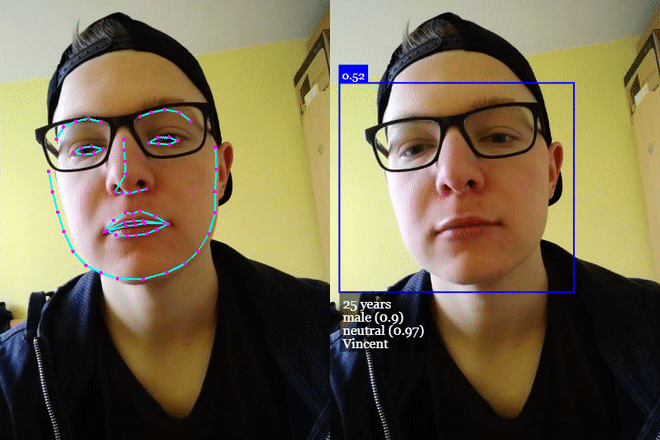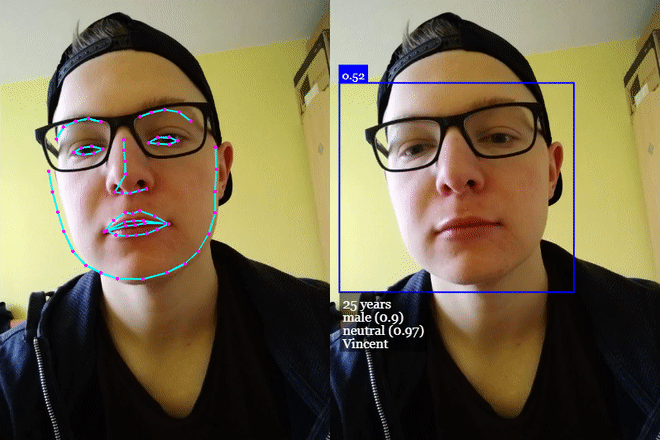
## **[Click me for Live Demos!](https://justadudewhohacks.github.io/face-api.js/)**
## Tutorials
* **[face-api.js — JavaScript API for Face Recognition in the Browser with tensorflow.js](https://itnext.io/face-api-js-javascript-api-for-face-recognition-in-the-browser-with-tensorflow-js-bcc2a6c4cf07)**
* **[Realtime JavaScript Face Tracking and Face Recognition using face-api.js’ MTCNN Face Detector](https://itnext.io/realtime-javascript-face-tracking-and-face-recognition-using-face-api-js-mtcnn-face-detector-d924dd8b5740)**
* **[Realtime Webcam Face Detection And Emotion Recognition - Video](https://youtu.be/CVClHLwv-4I)**
* **[Easy Face Recognition Tutorial With JavaScript - Video](https://youtu.be/AZ4PdALMqx0)**
* **[Using face-api.js with Vue.js and Electron](https://medium.com/@andreas.schallwig/do-not-laugh-a-simple-ai-powered-game-3e22ad0f8166)**
* **[Add Masks to People - Gant Laborde on Learn with Jason](https://www.learnwithjason.dev/fun-with-machine-learning-pt-2)**
## Table of Contents
* **[Features](#features)**
* **[Running the Examples](#running-the-examples)**
* **[face-api.js for the Browser](#face-api.js-for-the-browser)**
* **[face-api.js for Nodejs](#face-api.js-for-nodejs)**
* **[Usage](#getting-started)**
* **[Loading the Models](#getting-started-loading-models)**
* **[High Level API](#high-level-api)**
* **[Displaying Detection Results](#getting-started-displaying-detection-results)**
* **[Face Detection Options](#getting-started-face-detection-options)**
* **[Utility Classes](#getting-started-utility-classes)**
* **[Other Useful Utility](#other-useful-utility)**
* **[Available Models](#models)**
* **[Face Detection](#models-face-detection)**
* **[Face Landmark Detection](#models-face-landmark-detection)**
* **[Face Recognition](#models-face-recognition)**
* **[Face Expression Recognition](#models-face-expression-recognition)**
* **[Age Estimation and Gender Recognition](#models-age-and-gender-recognition)**
* **[API Documentation](https://justadudewhohacks.github.io/face-api.js/docs/globals.html)**
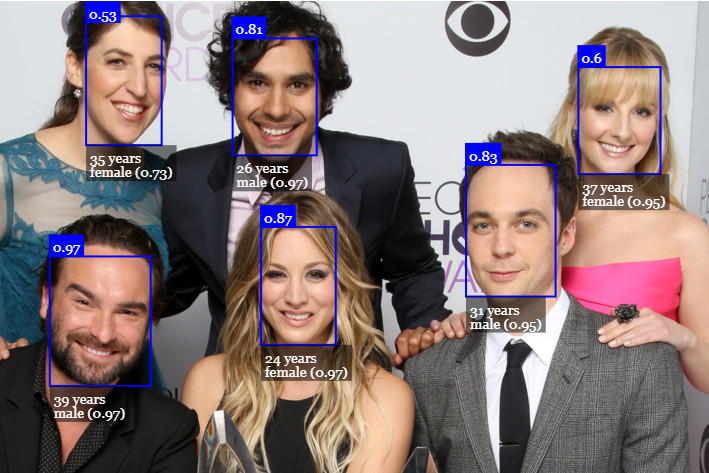
# Features
## Face Recognition
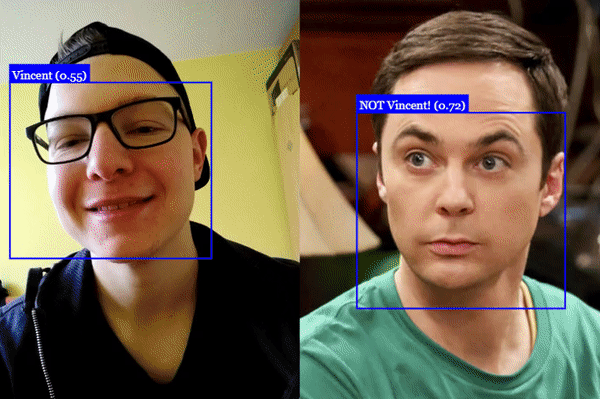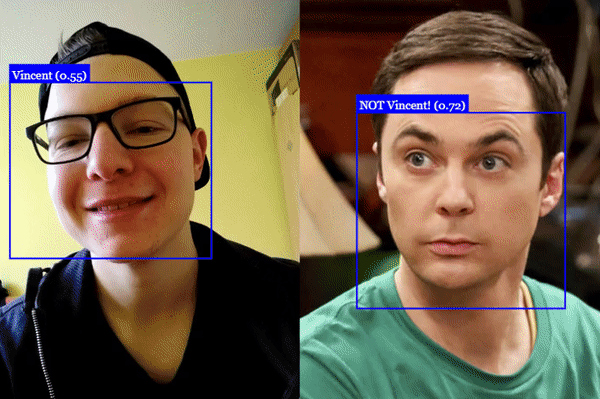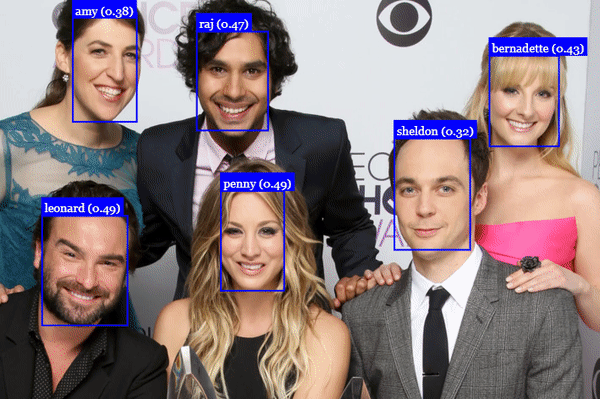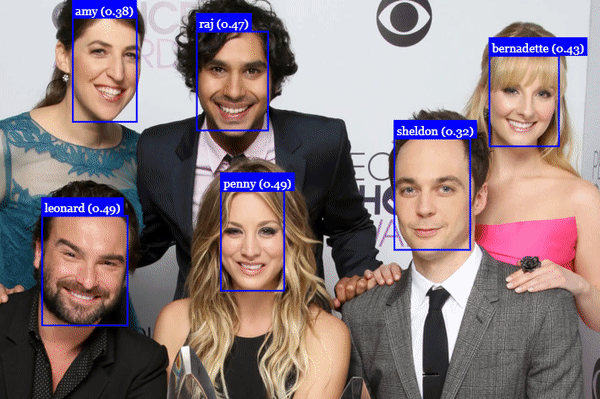
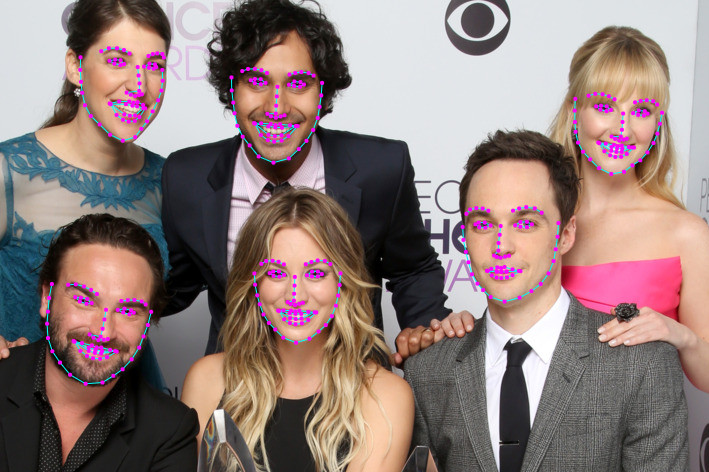
## Face Landmark Detection

## Face Expression Recognition

## Age Estimation & Gender Recognition
<a name="running-the-examples"></a>
# Running the Examples
Clone the repository:
``` bash
git clone https://github.com/justadudewhohacks/face-api.js.git
```
## Running the Browser Examples
``` bash
cd face-api.js/examples/examples-browser
npm i
npm start
```
Browse to http://localhost:3000/.
## Running the Nodejs Examples
``` bash
cd face-api.js/examples/examples-nodejs
npm i
```
Now run one of the examples using ts-node:
``` bash
ts-node faceDetection.ts
```
Or simply compile and run them with node:
``` bash
tsc faceDetection.ts
node faceDetection.js
```
<a name="face-api.js-for-the-browser"></a>
# face-api.js for the Browser
Simply include the latest script from [dist/face-api.js](https://github.com/justadudewhohacks/face-api.js/tree/master/dist).
Or install it via npm:
``` bash
npm i face-api.js
```
<a name="face-api.js-for-nodejs"></a>
# face-api.js for Nodejs
We can use the equivalent API in a nodejs environment by polyfilling some browser specifics, such as HTMLImageElement, HTMLCanvasElement and ImageData. The easiest way to do so is by installing the node-canvas package.
Alternatively you can simply construct your own tensors from image data and pass tensors as inputs to the API.
Furthermore you want to install @tensorflow/tfjs-node (not required, but highly recommended), which speeds things up drastically by compiling and binding to the native Tensorflow C++ library:
``` bash
npm i face-api.js canvas @tensorflow/tfjs-node
```
Now we simply monkey patch the environment to use the polyfills:
``` javascript
// import nodejs bindings to native tensorflow,
// not required, but will speed up things drastically (python required)
import '@tensorflow/tfjs-node';
// implements nodejs wrappers for HTMLCanvasElement, HTMLImageElement, ImageData
import * as canvas from 'canvas';
import * as faceapi from 'face-api.js';
// patch nodejs environment, we need to provide an implementation of
// HTMLCanvasElement and HTMLImageElement
const { Canvas, Image, ImageData } = canvas
faceapi.env.monkeyPatch({ Canvas, Image, ImageData })
```
<a name="getting-started"></a>
# Getting Started
<a name="getting-started-loading-models"></a>
## Loading the Models
All global neural network instances are exported via faceapi.nets:
``` javascript
console.log(faceapi.nets)
// ageGenderNet
// faceExpressionNet
// faceLandmark68Net
// faceLandmark68TinyNet
// faceRecognitionNet
// ssdMobilenetv1
// tinyFaceDetector
// tinyYolov2
```
To load a model, you have to provide the corresponding manifest.json file as well as the model weight files (shards) as assets. Simply copy them to your public or assets folder. The manifest.json and shard files of a model have to be located in the same directory / accessible under the same route.
Assuming the models reside in **public/models**:
``` javascript
await faceapi.nets.ssdMobilenetv1.loadFromUri('/models')
// accordingly for the other models:
// await faceapi.nets.faceLandmark68Net.loadFromUri('/models')
// await faceapi.nets.faceRecognitionNet.loadFromUri('/models')
// ...
```
In a nodejs environment you can furthermore load the models directly from disk:
``` javascript
await faceapi.nets.ssdMobilenetv1.loadFromDisk('./models')
```
You can also load the model from a tf.NamedTensorMap:
``` javascript
await faceapi.nets.ssdMobilenetv1.loadFromWeightMap(weightMap)
```
Alternatively, you can also create own instances of the neural nets:
``` javascript
const net = new faceapi.SsdMobilenetv1()
await net.loadFromUri('/models')
```
You can also load the weights as a Float32Array (in case you want to use the uncompressed models):
``` javascript
// using fetch
net.load(await faceapi.fetchNetWeights('/models/face_detection_model.weights'))
// using axios
const res = await axios.get('/models/face_detection_model.weights', { responseType: 'arraybuffer' })
const weights = new Float32Array(res.data)
net.load(weights)
```
<a name="getting-high-level-api"></a>
## High Level API
In the following **input** can be an HTML img, video or canvas element or the id of that element.
``` html
<img id="myImg" src="images/example.png" />
<video id="myVideo" src="media/example.mp4" />
<canvas id="myCanvas" />
```
``` javascript
const input = document.getElementById('myImg')
// const input = document.getElementById('myVideo')
// const input = document.getElementById('myCanvas')
// or simply:
// const input = 'myImg'
```
### Detecting Faces
Detect all faces in an image. Returns **Array<[FaceDetection](#interface-face-detection)>**:
``` javascript
const detections = await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input)
```
Detect the face with the highest confidence score in an image. Returns **[FaceDetection](#interface-face-detection) | undefined**:
``` javascript
const detection = await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input)
```
By default **detectAllFaces** and **detectSingleFace** utilize the SSD Mobilenet V1 Face Detector. You can specify the face detector by passing the corresponding options object:
``` javascript
const detections1 = await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input, new faceapi.SsdMobilenetv1Options())
const detections2 = await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input, new faceapi.TinyFaceDetectorOptions())
```
You can tune the options of each face detector as shown [here](#getting-started-face-detection-options).
### Detecting 68 Face Landmark Points
**After face detection, we can furthermore predict the facial landmarks for each detected face as follows:**
Detect all faces in an image + computes 68 Point Face Landmarks for each detected face. Returns **Array<[WithFaceLandmarks<WithFaceDetection<{}>>](#getting-started-utility-classes)>**:
``` javascript
const detectionsWithLandmarks = await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input).withFaceLandmarks()
```
Detect the face with the highest confidence score in an image + computes 68 Point Face Landmarks for that face. Returns **[WithFaceLandmarks<WithFaceDetection<{}>>](#getting-started-utility-classes) | undefined**:
``` javascript
const detectionWithLandmarks = await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input).withFaceLandmarks()
```
You can also specify to use the tiny model instead of the default model:
``` javascript
const useTinyModel = true
const detectionsWithLandmarks = await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input).withFaceLandmarks(useTinyModel)
```
### Computing Face Descriptors
**After face detection and facial landmark prediction the face descriptors for each face can be computed as follows:**
Detect all faces in an image + compute 68 Point Face Landmarks for each detected face. Returns **Array<[WithFaceDescriptor<WithFaceLandmarks<WithFaceDetection<{}>>>](#getting-started-utility-classes)>**:
``` javascript
const results = await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input).withFaceLandmarks().withFaceDescriptors()
```
Detect the face with the highest confidence score in an image + compute 68 Point Face Landmarks and face descriptor for that face. Returns **[WithFaceDescriptor<WithFaceLandmarks<WithFaceDetection<{}>>>](#getting-started-utility-classes) | undefined**:
``` javascript
const result = await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input).withFaceLandmarks().withFaceDescriptor()
```
### Recognizing Face Expressions
**Face expression recognition can be performed for detected faces as follows:**
Detect all faces in an image + recognize face expressions of each face. Returns **Array<[WithFaceExpressions<WithFaceLandmarks<WithFaceDetection<{}>>>](#getting-started-utility-classes)>**:
``` javascript
const detectionsWithExpressions = await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input).withFaceLandmarks().withFaceExpressions()
```
Detect the face with the highest confidence score in an image + recognize the face expressions for that face. Returns **[WithFaceExpressions<WithFaceLandmarks<WithFaceDetection<{}>>>](#getting-started-utility-classes) | undefined**:
``` javascript
const detectionWithExpressions = await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input).withFaceLandmarks().withFaceExpressions()
```
**You can also skip .withFaceLandmarks(), which will skip the face alignment step (less stable accuracy):**
Detect all faces without face alignment + recognize face expressions of each face. Returns **Array<[WithFaceExpressions<WithFaceDetection<{}>>](#getting-started-utility-classes)>**:
``` javascript
const detectionsWithExpressions = await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input).withFaceExpressions()
```
Detect the face with the highest confidence score without face alignment + recognize the face expression for that face. Returns **[WithFaceExpressions<WithFaceDetection<{}>>](#getting-started-utility-classes) | undefined**:
``` javascript
const detectionWithExpressions = await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input).withFaceExpressions()
```
### Age Estimation and Gender Recognition
**Age estimation and gender recognition from detected faces can be done as follows:**
Detect all faces in an image + estimate age and recognize gender of each face. Returns **Array<[WithAge<WithGender<WithFaceLandmarks<WithFaceDetection<{}>>>>](#getting-started-utility-classes)>**:
``` javascript
const detectionsWithAgeAndGender = await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input).withFaceLandmarks().withAgeAndGender()
```
Detect the face with the highest confidence score in an image + estimate age and recognize gender for that face. Returns **[WithAge<WithGender<WithFaceLandmarks<WithFaceDetection<{}>>>>](#getting-started-utility-classes) | undefined**:
``` javascript
const detectionWithAgeAndGender = await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input).withFaceLandmarks().withAgeAndGender()
```
**You can also skip .withFaceLandmarks(), which will skip the face alignment step (less stable accuracy):**
Detect all faces without face alignment + estimate age and recognize gender of each face. Returns **Array<[WithAge<WithGender<WithFaceDetection<{}>>>](#getting-started-utility-classes)>**:
``` javascript
const detectionsWithAgeAndGender = await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input).withAgeAndGender()
```
Detect the face with the highest confidence score without face alignment + estimate age and recognize gender for that face. Returns **[WithAge<WithGender<WithFaceDetection<{}>>>](#getting-started-utility-classes) | undefined**:
``` javascript
const detectionWithAgeAndGender = await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input).withAgeAndGender()
```
### Composition of Tasks
**Tasks can be composed as follows:**
``` javascript
// all faces
await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input)
await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input).withFaceExpressions()
await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input).withFaceLandmarks()
await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input).withFaceLandmarks().withFaceExpressions()
await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input).withFaceLandmarks().withFaceExpressions().withFaceDescriptors()
await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input).withFaceLandmarks().withAgeAndGender().withFaceDescriptors()
await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input).withFaceLandmarks().withFaceExpressions().withAgeAndGender().withFaceDescriptors()
// single face
await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input)
await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input).withFaceExpressions()
await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input).withFaceLandmarks()
await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input).withFaceLandmarks().withFaceExpressions()
await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input).withFaceLandmarks().withFaceExpressions().withFaceDescriptor()
await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input).withFaceLandmarks().withAgeAndGender().withFaceDescriptor()
await faceapi.detectSingleFace(input).withFaceLandmarks().withFaceExpressions().withAgeAndGender().withFaceDescriptor()
```
### Face Recognition by Matching Descriptors
To perform face recognition, one can use faceapi.FaceMatcher to compare reference face descriptors to query face descriptors.
First, we initialize the FaceMatcher with the reference data, for example we can simply detect faces in a **referenceImage** and match the descriptors of the detected faces to faces of subsequent images:
``` javascript
const results = await faceapi
.detectAllFaces(referenceImage)
.withFaceLandmarks()
.withFaceDescriptors()
if (!results.length) {
return
}
// create FaceMatcher with automatically assigned labels
// from the detection results for the reference image
const faceMatcher = new faceapi.FaceMatcher(results)
```
Now we can recognize a persons face shown in **queryImage1**:
``` javascript
const singleResult = await faceapi
.detectSingleFace(queryImage1)
.withFaceLandmarks()
.withFaceDescriptor()
if (singleResult) {
const bestMatch = faceMatcher.findBestMatch(singleResult.descriptor)
console.log(bestMatch.toString())
}
```
Or we can recognize all faces shown in **queryImage2**:
``` javascript
const results = await faceapi
.detectAllFaces(queryImage2)
.withFaceLandmarks()
.withFaceDescriptors()
results.forEach(fd => {
const bestMatch = faceMatcher.findBestMatch(fd.descriptor)
console.log(bestMatch.toString())
})
```
You can also create labeled reference descriptors as follows:
``` javascript
const labeledDescriptors = [
new faceapi.LabeledFaceDescriptors(
'obama',
[descriptorObama1, descriptorObama2]
),
new faceapi.LabeledFaceDescriptors(
'trump',
[descriptorTrump]
)
]
const faceMatcher = new faceapi.FaceMatcher(labeledDescriptors)
```
<a name="getting-started-displaying-detection-results"></a>
## Displaying Detection Results
Preparing the overlay canvas:
``` javascript
const displaySize = { width: input.width, height: input.height }
// resize the overlay canvas to the input dimensions
const canvas = document.getElementById('overlay')
faceapi.matchDimensions(canvas, displaySize)
```
face-api.js predefines some highlevel drawing functions, which you can utilize:
``` javascript
/* Display detected face bounding boxes */
const detections = await faceapi.detectAllFaces(input)
// resize the detected boxes in case your displayed image has a different size than the original
const resizedDetections = faceapi.resizeResults(detections, displaySize)
// draw detections into the canvas
faceapi.draw.drawDetections(canvas, resizedDetections)
/* Display face landmarks */
const detectionsWithLandmarks = await faceapi
.detectAllFaces(input)
.withFaceLandmarks()
// resize the detected boxes and landmarks in case your displayed image has a different size than the original
const resizedResults = faceapi.resizeResults(detectionsWithLandmarks, displaySize)
// draw detections into the canvas
faceapi.draw.drawDetections(canvas, resizedResults)
// draw the landmarks into the canvas
faceapi.draw.drawFaceLandmarks(canvas, resizedResults)
/* Display face expression results */
const detectionsWithExpressions = await faceapi
.detectAllFaces(input)
.withFaceLandmarks()
.withFaceExpressions()
// resize the detected boxes and landmarks in case your displayed image has a different size than the original
const resizedResults = faceapi.resizeResults(detectionsWithExpressions, displaySize)
// draw detections into the canvas
faceapi.draw.drawDetections(canvas, resizedResults)
// draw a textbox displaying the face expressions with minimum probability into the canvas
const minProbability = 0.05
faceapi.draw.drawFaceExpressions(canvas, resizedResults, minProbability)
```
You can also draw boxes with custom text ([DrawBox](https://github.com/justadudewhohacks/tfjs-image-recognition-base/blob/master/src/draw/DrawBox.ts)):
``` javascript
const box = { x: 50, y: 50, width: 100, height: 100 }
// see DrawBoxOptions below
const drawOptions = {
label: 'Hello I am a box!',
lineWidth: 2
}
const drawBox = new faceapi.draw.DrawBox(box, drawOptions)
drawBox.draw(document.getElementById('myCanvas'))
```
DrawBox drawing options:
``` javascript
export interface IDrawBoxOptions {
boxColor?: string
lineWidth?: number
drawLabelOptions?: IDrawTextFieldOptions
label?: string
}
```
Finally you can draw custom text fields ([DrawTextField](https://github.com/justadudewhohacks/tfjs-image-recognition-base/blob/master/src/draw/DrawTextField.ts)):
``` javascript
const text = [
'This is a textline!',
'This is another textline!'
]
const anchor = { x: 200, y: 200 }
// see DrawTextField below
const drawOptions = {
anchorPosition: 'TOP_LEFT',
backgroundColor: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)'
}
const drawBox = new faceapi.draw.DrawTextField(text, anchor, drawOptions)
drawBox.draw(document.getElementById('myCanvas'))
```
DrawTextField drawing options:
``` javascript
export interface IDrawTextFieldOptions {
anchorPosition?: AnchorPosition
backgroundColor?: string
fontColor?: string
fontSize?: number
fontStyle?: string
padding?: number
}
export enum AnchorPosition {
TOP_LEFT = 'TOP_LEFT',
TOP_RIGHT = 'TOP_RIGHT',
BOTTOM_LEFT = 'BOTTOM_LEFT',
BOTTOM_RIGHT = 'BOTTOM_RIGHT'
}
```
<a name="getting-started-face-detection-options"></a>
## Face Detection Options
### SsdMobilenetv1Options
``` javascript
export interface ISsdMobilenetv1Options {
// minimum confidence threshold
// default: 0.5
minConfidence?: number
// maximum number of faces to return
// default: 100
maxResults?: number
}
// example
const options = new faceapi.SsdMobilenetv1Options({ minConfidence: 0.8 })
```
### TinyFaceDetectorOptions
``` javascript
export interface ITinyFaceDetectorOptions {
// size at which image is processed, the smaller the faster,
// but less precise in detecting smaller faces, must be divisible
// by 32, common sizes are 128, 160, 224, 320, 416, 512, 608,
// for face tracking via webcam I would recommend using smaller sizes,
// e.g. 128, 160, for detecting smaller faces use larger sizes, e.g. 512, 608
// default: 416
inputSize?: number
// minimum confidence threshold
// default: 0.5
scoreThreshold?: number
}
// example
const options = new faceapi.TinyFaceDetectorOptions({ inputSize: 320 })
```
<a name="getting-started-utility-classes"></a>
## Utility Classes
### IBox
``` javascript
export interface IBox {
x: number
y: number
width: number
height: number
}
```
### IFaceDetection
``` javascript
export interface IFaceDetection {
score: number
box: Box
}
```
### IFaceLandmarks
``` javascript
export interface IFaceLandmarks {
positions: Point[]
shift: Point
}
```
### WithFaceDetection
``` javascript
export type WithFaceDetection<TSource> = TSource & {
detection: FaceDetection
}
```
### WithFaceLandmarks
``` javascript
export type WithFaceLandmarks<TSource> = TSource & {
unshiftedLandmarks: FaceLandmarks
landmarks: FaceLandmarks
alignedRect: FaceDetection
}
```
### WithFaceDescriptor
``` javascript
export type WithFaceDescriptor<TSource> = TSource & {
descriptor: Float32Array
}
```
### WithFaceExpressions
``` javascript
export type WithFaceExpressions<TSource> = TSource & {
expressions: FaceExpressions
}
```
### WithAge
``` javascript
export type WithAge<TSource> = TSource & {
age: number
}
```
### WithGender
``` javascript
export type WithGender<TSource> = TSource & {
gender: Gender
genderProbability: number
}
export enum Gender {
FEMALE = 'female',
MALE = 'male'
}
```
<a name="getting-started-other-useful-utility"></a>
## Other Useful Utility
### Using the Low Level API
Instead of using the high level API, you can directly use the forward methods of each neural network:
``` javascript
const detections1 = await faceapi.ssdMobilenetv1(input, options)
const detections2 = await faceapi.tinyFaceDetector(input, options)
const landmarks1 = await faceapi.detectFaceLandmarks(faceImage)
const landmarks2 = await faceapi.detectFaceLandmarksTiny(faceImage)
const descriptor = await faceapi.computeFaceDescriptor(alignedFaceImage)
```
### Extracting a Canvas for an Image Region
``` javascript
const regionsToExtract = [
new faceapi.Rect(0, 0, 100, 100)
]
// actually extractFaces is meant to extract face regions from bounding boxes
// but you can also use it to extract any other region
const canvases = await faceapi.extractFaces(input, regionsToExtract)
```
### Euclidean Distance
``` javascript
// ment to be used for computing the euclidean distance between two face descriptors
const dist = faceapi.euclideanDistance([0, 0], [0, 10])
console.log(dist) // 10
```
### Retrieve the Face Landmark Points and Contours
``` javascript
const landmarkPositions = landmarks.positions
// or get the positions of individual contours,
// only available for 68 point face ladnamrks (FaceLandmarks68)
const jawOutline = landmarks.getJawOutline()
const nose = landmarks.getNose()
const mouth = landmarks.getMouth()
const leftEye = landmarks.getLeftEye()
const rightEye = landmarks.getRightEye()
const leftEyeBbrow = landmarks.getLeftEyeBrow()
const rightEyeBrow = landmarks.getRightEyeBrow()
```
### Fetch and Display Images from an URL
``` html
<img id="myImg" src="">
```
``` javascript
const image = await faceapi.fetchImage('/images/example.png')
console.log(image instanceof HTMLImageElement) // true
// displaying the fetched image content
const myImg = document.getElementById('myImg')
myImg.src = image.src
```
### Fetching JSON
``` javascript
const json = await faceapi.fetchJson('/files/example.json')
```
### Creating an Image Picker
``` html
<img id="myImg" src="">
<input id="myFileUpload" type="file" onchange="uploadImage()" accept=".jpg, .jpeg, .png">
```
``` javascript
async function uploadImage() {
const imgFile = document.getElementById('myFileUpload').files[0]
// create an HTMLImageElement from a Blob
const img = await faceapi.bufferToImage(imgFile)
document.getElementById('myImg').src = img.src
}
```
### Creating a Canvas Element from an Image or Video Element
``` html
<img id="myImg" src="images/example.png" />
<video id="myVideo" src="media/example.mp4" />
```
``` javascript
const canvas1 = faceapi.createCanvasFromMedia(document.getElementById('myImg'))
const canvas2 = faceapi.createCanvasFromMedia(document.getElementById('myVideo'))
```
<a name="models"></a>
# Available Models
<a name="models-face-detection"></a>
## Face Detection Models
### SSD Mobilenet V1
For face detection, this project implements a SSD (Single Shot Multibox Detector) based on MobileNetV1. The neural net will compute the locations of each face in an image and will return the bounding boxes together with it's probability for each face. This face detector is aiming towards obtaining high accuracy in detecting face bounding boxes instead of low inference time. The size of the quantized model is about 5.4 MB (**ssd_mobilenetv1_model**).
The face detection model has been trained on the [WIDERFACE dataset](http://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/WIDERFace/) and the weights are provided by [yeephycho](https://github.com/yeephycho) in [this](https://github.com/yeephycho/tensorflow-face-detection) repo.
### Tiny Face Detector
The Tiny Face Detector is a very performant, realtime face detector, which is much faster, smaller and less resource consuming compared to the SSD Mobilenet V1 face detector, in return it performs slightly less well on detecting small faces. This model is extremely mobile and web friendly, thus it should be your GO-TO face detector on mobile devices and resource limited clients. The size of the quantized model is only 190 KB (**tiny_face_detector_model**).
The face detector has been trained on a custom dataset of ~14K images labeled with bounding boxes. Furthermore the model has been trained to predict bounding boxes, which entirely cover facial feature points, thus it in general produces better results in combination with subsequent face landmark detection than SSD Mobilenet V1.
This model is basically an even tinier version of Tiny Yolo V2, replacing the regular convolutions of Yolo with depthwise separable convolutions. Yolo is fully convolutional, thus can easily adapt to different input image sizes to trade off accuracy for performance (inference time).
<a name="models-face-landmark-detection"></a>
## 68 Point Face Landmark Detection Models
This package implements a very lightweight and fast, yet accurate 68 point face landmark detector. The default model has a size of only 350kb (**face_landmark_68_model**) and the tiny model is only 80kb (**face_landmark_68_tiny_model**). Both models employ the ideas of depthwise separable convolutions as well as densely connected blocks. The models have been trained on a dataset of ~35k face images labeled with 68 face landmark points.
<a name="models-face-recognition"></a>
## Face Recognition Model
For face recognition, a ResNet-34 like architecture is implemented to compute a face descriptor (a feature vector with 128 values) from any given face image, which is used to describe the characteristics of a persons face. The model is **not** limited to the set of faces used for training, meaning you can use it for face recognition of any person, for example yourself. You can determine the similarity of two arbitrary faces by comparing their face descriptors, for example by computing the euclidean distance or using any other classifier of your choice.
The neural net is equivalent to the **FaceRecognizerNet** used in [face-recognition.js](https://github.com/justadudewhohacks/face-recognition.js) and the net used in the [dlib](https://github.com/davisking/dlib/blob/master/examples/dnn_face_recognition_ex.cpp) face recognition example. The weights have been trained by [davisking](https://github.com/davisking) and the model achieves a prediction accuracy of 99.38% on the LFW (Labeled Faces in the Wild) benchmark for face recognition.
The size of the quantized model is roughly 6.2 MB (**face_recognition_model**).
<a name="models-face-expression-recognition"></a>
## Face Expression Recognition Model
The face expression recognition model is lightweight, fast and provides reasonable accuracy. The model has a size of roughly 310kb and it employs depthwise separable convolutions and densely connected blocks. It has been trained on a variety of images from publicly available datasets as well as images scraped from the web. Note, that wearing glasses might decrease the accuracy of the prediction results.
<a name="models-age-and-gender-recognition"></a>
## Age and Gender Recognition Model
The age and gender recognition model is a multitask network, which employs a feature extraction layer, an age regression layer and a gender classifier. The model has a size of roughly 420kb and the feature extractor employs a tinier but very similar architecture to Xception.
This model has been trained and tested on the following databases with an 80/20 train/test split each: UTK, FGNET, Chalearn, Wiki, IMDB*, CACD*, MegaAge, MegaAge-Asian. The `*` indicates, that these databases have been algorithmically cleaned up, since the initial databases are very noisy.
### Total Test Results
Total MAE (Mean Age Error): **4.54**
Total Gender Accuracy: **95%**
### Test results for each database
The `-` indicates, that there are no gender labels available for these databases.
Database | UTK | FGNET | Chalearn | Wiki | IMDB* | CACD* | MegaAge | MegaAge-Asian |
----------------|-------:|------:|---------:|-----:|------:|------:|--------:|--------------:|
MAE | 5.25 | 4.23 | 6.24 | 6.54 | 3.63 | 3.20 | 6.23 | 4.21 |
Gender Accuracy | 0.93 | - | 0.94 | 0.95 | - | 0.97 | - | - |
### Test results for different age category groups
Age Range | 0 - 3 | 4 - 8 | 9 - 18 | 19 - 28 | 29 - 40 | 41 - 60 | 60 - 80 | 80+ |
----------------|-------:|------:|-------:|--------:|--------:|--------:|--------:|--------:|
MAE | 1.52 | 3.06 | 4.82 | 4.99 | 5.43 | 4.94 | 6.17 | 9.91 |
Gender Accuracy | 0.69 | 0.80 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.9 |